VETIVER (Vetiveria zizanioides Linn.): AN AROMATIC GRASS USE FOR FLOOD AND STREAM BANK EROSION CONTROL
Souvick Banik, Ameda Swarnalata and C. S. Karthik
Ph.D. Research Scholars, Bidhan Chandra Krishi Vishwavidyalaya, West Bengal
Vetiver (Vetiveria zizanioides Linn.) is a tall, fast growing perennial grass native to India which is now extensively used for erosion and flood control in over 70 countries worldwide. It is generally distributed widely in tropical Asia, Africa and Australia. It is a obligatory cross pollinated crop. Vetiver grass is a C4 perennial grass that fits well in ecosystem service model contributing to local and national economies for its multifarious environmental applications, and offers sustainable opportunities for carbon sequestration. Vetiver grass has been used for degraded land reclamation, erosion control and slope stabilization for centuries and its popularity has increased remarkably in the last decades in many parts of the world and also India . India produces the best quality vetiver oil in the world and has the potential to export .
SYSTEMATICS
Kingdom: Plantae
Clade: Angiosperms
Clade: Monocots
Clade: Commelinids
Order: Poales
Family: Poaceae
Genus: Chrysopogon
Species: C. zizanioides
Vetiver is a Tough Plant against the Soil erosion:
It have the ability to resist a deep drought for up to eighteen months, Vetiver is just as flexible when it is submerged and can remain under water for up to three months without damage. The plants grow readily to approximately 60cm wide and up to a maximum of 180cm tall, never exceeding these dimensions. Once they reach maturity at around three years old they can be grazed right to the ground and will spring happily away again. Stock generally do not prefer it to grass, although some cows love it, but they will readily eat it when more appealing feed isn’t available. It does them no harm and provides feed in drought conditions.
Vetiver – Fungicide and Pesticide :
Vetiver is a well-known flea repellent in some countries and is used as a fungicide as well as a pesticide. Grown near other crops, it protects them from fungal and pest attack.
Vetiver System use as flood and stream Bank Erosion
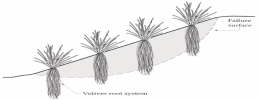
The Vetiver System is a developing technology. The Vetiver System (VS) is a system of soil and water conservation whose main component is the use of the vetiver plant in hedgerows. The Vetiver System is used in more than 100 countries for soil and water conservation, infrastructure stabilization, pollution control, waste water treatment, mitigation and rehabilitation, sediment control, prevention of storm damage and other environmental protection applications (through bioengineering and phytoremediation). When Vetiver is planted as a hedgerow across a slope, it forms a dense vegetative barrier that slows and spreads rainfall runoff. Combined with a deep and strong root system, a wide range of pH tolerance (from about pH 3 to pH 11), a high tolerance to most heavy metals, an ability to remove from soil and water large quantities of nitrates, phosphates and farm chemicals, the vetiver plant can be used for soil and water conservation, engineered construction site stabilization, pollution control (constructed wetlands), and other uses where soil and water come together. A good hedge reduces rainfall runoff by as much as 70% and sediment by as much as 90%. A hedgerow stays where it is planted and the sediment that is spread out behind the hedgerow gradually accumulates to form a long-lasting terrace. It is a low-cost, labour-intensive technology claimed to have a high benefit/cost ratio. When used for civil works protection, its cost is claimed to be about 1/20 of traditional engineered systems and designs.
Vetiver : Use as Perfume Ingredient and handicrafts
It is also a well-known ingredient in perfume manufacture and as well as handicraft manufacturing.
Reference:
National Academy, Panel on Vetiver. "Vetiver: A Thin Green Line against Erosion". Catalogue, National Academies Press. National Academies Press. Retrieved 4 May 2018.
"Vetiver Grass: A Thin Green Line Against Erosion". National Academies Press. 1993. Retrieved 2017-12-15.
P. Truong; T. Tan Van; E. Pinners (2008). Vetiver Systems Application, Technical Reference Manual. The Vetiver Network International. p. 89.
Souvick Banik, Ameda Swarnalata and C. S. Karthik
Ph.D. Research Scholars, Bidhan Chandra Krishi Vishwavidyalaya, West Bengal
Vetiver (Vetiveria zizanioides Linn.) is a tall, fast growing perennial grass native to India which is now extensively used for erosion and flood control in over 70 countries worldwide. It is generally distributed widely in tropical Asia, Africa and Australia. It is a obligatory cross pollinated crop. Vetiver grass is a C4 perennial grass that fits well in ecosystem service model contributing to local and national economies for its multifarious environmental applications, and offers sustainable opportunities for carbon sequestration. Vetiver grass has been used for degraded land reclamation, erosion control and slope stabilization for centuries and its popularity has increased remarkably in the last decades in many parts of the world and also India . India produces the best quality vetiver oil in the world and has the potential to export .
SYSTEMATICS
Kingdom: Plantae
Clade: Angiosperms
Clade: Monocots
Clade: Commelinids
Order: Poales
Family: Poaceae
Genus: Chrysopogon
Species: C. zizanioides
Vetiver is a Tough Plant against the Soil erosion:
It have the ability to resist a deep drought for up to eighteen months, Vetiver is just as flexible when it is submerged and can remain under water for up to three months without damage. The plants grow readily to approximately 60cm wide and up to a maximum of 180cm tall, never exceeding these dimensions. Once they reach maturity at around three years old they can be grazed right to the ground and will spring happily away again. Stock generally do not prefer it to grass, although some cows love it, but they will readily eat it when more appealing feed isn’t available. It does them no harm and provides feed in drought conditions.
Vetiver – Fungicide and Pesticide :
Vetiver is a well-known flea repellent in some countries and is used as a fungicide as well as a pesticide. Grown near other crops, it protects them from fungal and pest attack.
Vetiver System use as flood and stream Bank Erosion
The Vetiver System is a developing technology. The Vetiver System (VS) is a system of soil and water conservation whose main component is the use of the vetiver plant in hedgerows. The Vetiver System is used in more than 100 countries for soil and water conservation, infrastructure stabilization, pollution control, waste water treatment, mitigation and rehabilitation, sediment control, prevention of storm damage and other environmental protection applications (through bioengineering and phytoremediation). When Vetiver is planted as a hedgerow across a slope, it forms a dense vegetative barrier that slows and spreads rainfall runoff. Combined with a deep and strong root system, a wide range of pH tolerance (from about pH 3 to pH 11), a high tolerance to most heavy metals, an ability to remove from soil and water large quantities of nitrates, phosphates and farm chemicals, the vetiver plant can be used for soil and water conservation, engineered construction site stabilization, pollution control (constructed wetlands), and other uses where soil and water come together. A good hedge reduces rainfall runoff by as much as 70% and sediment by as much as 90%. A hedgerow stays where it is planted and the sediment that is spread out behind the hedgerow gradually accumulates to form a long-lasting terrace. It is a low-cost, labour-intensive technology claimed to have a high benefit/cost ratio. When used for civil works protection, its cost is claimed to be about 1/20 of traditional engineered systems and designs.
Vetiver : Use as Perfume Ingredient and handicrafts
It is also a well-known ingredient in perfume manufacture and as well as handicraft manufacturing.
Reference:
National Academy, Panel on Vetiver. "Vetiver: A Thin Green Line against Erosion". Catalogue, National Academies Press. National Academies Press. Retrieved 4 May 2018.
"Vetiver Grass: A Thin Green Line Against Erosion". National Academies Press. 1993. Retrieved 2017-12-15.
P. Truong; T. Tan Van; E. Pinners (2008). Vetiver Systems Application, Technical Reference Manual. The Vetiver Network International. p. 89.